Samsung Electronics заключает уже второй контракт на производство 8-нм графических чипов семейства Ampere по заказу NVIDIA. Предыдущее соглашение было заключено в сентябре уходящего года.
Вэб-портал газеты The Korea Economic Daily накануне сообщил о соглашении по новому контракту между Samsung и знаменитой американской компанией, чей головной офис находится в Санта-Кларе (штат Калифорния). Условия сделки не уточняются, но в пресс-релизе говорится о производстве 8-нм графических процессоров игрового назначения, а сумма контракта оценивается экспертами в сотни миллионов долларов США. Эта новость оказала положительное влияние на репутацию Samsung Electronics. В результате акции конкурирующей TSMC просели на 0,3 %, что означает первую, пусть и не очень значительную, реакцию рынка на возможный переход крупных заказчиков к Samsung в обозримой перспективе.
Южнокорейский электронный гигант будет выпускать графические процессоры NVIDIA на своём флагманском предприятии в Хвасоне. Возможно, новый контракт предусматривает увеличенные объёмы производства, и с его помощью NVIDIA постарается устранить дефицит видеокарт семейства GeForce RTX 30, который наблюдается уже несколько месяцев. Тем более, что на подходе мобильное семейство Ampere, и дополнительные мощности потребовались бы в любом случае.
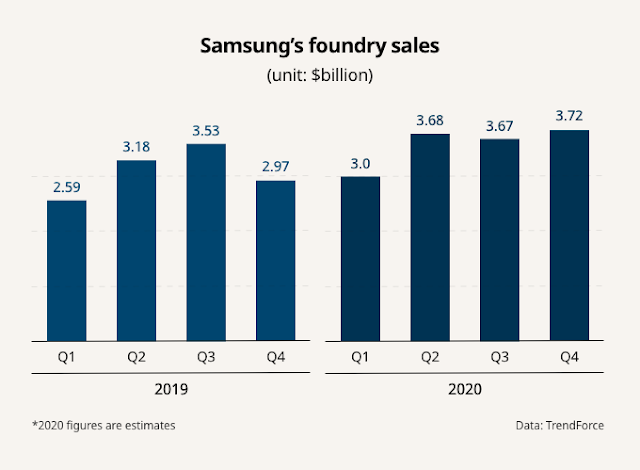
По оценкам TrendForce, в этом году контрактный бизнес подразделения Samsung Foundry позволил увеличить выручку на 17,9 %, до $14,05 миллиарда. Помимо NVIDIA и Qualcomm, клиентами Samsung стали Google, IBM, Cisco и китайская Baidu. Мобильные чипы для Qualcomm корейский подрядчик тоже изготавливает по 8-нм технологии. Сейчас Samsung располагает семью производственными линиями для обслуживания сторонних заказчиков, которые расположены в Южной Корее и США. Доля техногиганта на мировом рынке контрактного производства чипов возросла до 16,4%.
В статье The Korea Economic Daily говорится, что Samsung не собирается останавливаться на достигнутом и будет расширять это направление за счёт ввода новых мощностей (в том числе строительства очередного завода на производственном комплексе в Остине, США) и освоения более совершенных техпроцессов, включая 4-нм с использованием экстремального ультрафиолетового экспонирования (EUV). Это позволит значительно сократить отставание от TSMC в контрактном полупроводниковом бизнесе и привлечь новых клиентов.
По данным отраслевых источников, Samsung ежегодно тратит по 10 триллионов вон (8,6 миллиарда долларов) на разработку технологий производства микросхем и приобретение соответствующего оборудования.
Samsung clinches 2nd deal to make Nvidia’s latest gaming chips
Samsung Electronics Co. will manufacture Nvidia Corp.’s latest gaming chips in the second such contract of the year from the US chipmaker, as the South Korean tech giant aims to expand its presence in the foundry business.
Samsung, the world’s second-largest foundry player, has clinched a deal to make Nvidia’s next-generation graphic processing unit (GPU), the Ampere GeForce RTX30 series, using its 8-nanometer process technology, according to the semiconductor industry on Dec. 17.
The contract is Samsung’s second order this year from the Santa Clara, California-based company, following a similar deal in September.
The value of the latest deal is unknown but the industry estimates the contract is worth hundreds of billions of won. Samsung is expected to make the gaming chips at its Hwaseong plant.
Analysts said the contract is significant in that Samsung won the deal amid market talk that Nvidia’s new GPU has been in tight supply due to unsatisfactory 8 nm process yield rates at its foundry partner Samsung, raising speculation that the US company may award the contract to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC), the industry leader.
Industry officials said Nvidia has favored Samsung over TSMC in consideration of Samsung’s technology and the need for quick delivery of the chips. The RTX3080, priced at $699, the same as its previous model, has been in high demand because of its faster data processing speed.
Samsung has been stepping up efforts to enhance its presence in the global foundry market as specialty DRAM prices are expected to continue their rally into next year amid tight supply.
Earlier this month, Samsung announced a leadership change in its two key businesses, memory chips and foundry, as part of its bid to gain further ground in the global chipmaking sector.
Analysts said Samsung’s new foundry chief Choi Si-young will be asked to narrow the gap with TSMC in coming years.
According to market researcher TrendForce, Samsung’s foundry business is expected to post a record $14.05 billion in sales this year, up 17.9% from 2019, as the company is expanding its client base beyond Nvidia to Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Google, IBM, Cisco and China’s Baidu.
In October, Samsung signed a deal to make mobile chips for Qualcomm, using its 8 nm technology.
To advance its technological leadership, Samsung has introduced an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography technology for 7 nm and finer products.
“Through the more advanced 4 nm processing node, we’ll further narrow the gap with TSMC,” said Samsung’s foundry chief Choi.
More recently, Samsung has purchased a giant lot of land in Austin, Texas, where its US chip plant is located, raising expectations that the company may expand its foundry business.
Samsung is known to be spending 10 trillion won ($8.6 billion) a year to develop chip foundry technology and purchase related equipment to close in on its bigger rival TSMC.
Currently, Samsung operates seven foundry production lines in Korea and the US.
Samsung’s market share in the global foundry industry is estimated at 16.4% as of the fourth quarter of 2020, following TSMC’s 55.6, according to TrendForce.