Samsung Electronics намерен инвестировать более $10 миллиардов в строительство нового завода по производству чипов в Остине (штат Техас, США). Об этом информационному агентству Bloomberg стало известно от нескольких отраслевых источников, пожелавших сохранить конфиденциальность.
По их словам, южнокорейский гигант намерен привлечь больше американских клиентов за счёт реализации этого проекта и догнать лидера рынка услуг по контрактному производству микросхем Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC).
Собеседники информагентства говорят, что в настоящее время Samsung ведёт переговоры относительно месторасположения предприятия в Остине, которое, как ожидается, будет выпускать чипы с технологическим процессом до 3нм. Согласно инсайдерской информации, пока речь идёт о предварительных планах, которые в итоге могут быть изменены. В Samsung подтвердили, что никаких окончательных решений ещё не принято.
По данным источников Bloomberg, Samsung рассчитывает начать строительство фабрики в 2021 году, установить большую часть оборудования - в 2022-м, а окончательный запуск осуществить в начале 2023-го. Итоговую сумму инвестиций ещё предстоит определить, но на данный момент речь идёт, по меньшей мере, о $10 миллиардах, сообщили источники Bloomberg.
Если Samsung реализует упомянутый проект, то в США появится первый завод по производству микросхем с использованием ультрафиолетовой литографии (EUV) - передовой технологии, которую южнокорейская корпорация уже использует для производства микросхем следующего поколения. На данный момент Samsung обладает двумя фабриками с технологией EUV - в Хвасоне и в Пхёнтхэке, Южная Корея.
Выгоду от строительства предприятия в Техасе получит не только Samsung, но и правительство США. Последнее заинтересовано в перенаправлении потоков занятости обратно в свою страну из Азии, куда ранее переместилась большая часть мирового производства в передовых отраслях за последние 20 лет.
Южнокорейский техногигант даже нанял лоббистов в Вашингтоне с целью получения налоговых льгот и субсидий от новой американской администрации. Тем не менее, Samsung хочет добиться сделки, даже если и не получит серьёзных стимулов от правительства.
"Если Samsung действительно хочет стать ведущим в мире производителем чипов к 2030 году, ему нужны огромные инвестиции в США, чтобы догнать TSMC, - говорит старший вице-президент HMC Securities Грег Ро (Greg Roh). - Скорее всего, TSMC реализует планы по постепенному внедрению техпроцесса 3 нм на своём заводе в Аризоне, и Samsung может сделать то же самое. Одной из самых сложных задач сейчас является получение EUV-оборудования, при том что Hynix и Micron также стремятся приобрести эти машины". Однако Samsung традиционно является приоритетным клиентом у нидерландской ASML, производящей литографические машины, поскольку является не только крупным заказчиком, но и акционером.
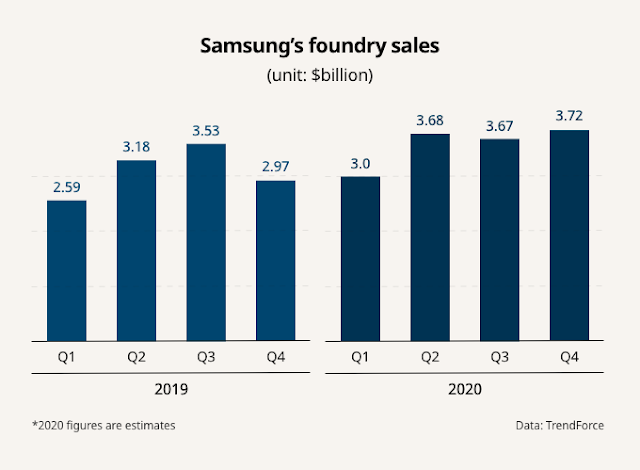
Ранее TSMC объявила о строительстве полупроводниковой фабрики в Аризоне (США), в которую планирует вложить порядка 12 млрд долларов. Запуск этого предприятия намечен на 2024 год. Однако Samsung намерен только в этом году вложить в свой полупроводниковый бизнес прядка $30 миллиардов, значительно опередив по темпу инвестиций тайваньских конкурентов.
Samsung expands Texas chip plant in investment race with TSMC
Samsung Electronics Co. is considering spending more than $10 billion building its most advanced logic chipmaking plant in the U.S., a major investment it hopes will win more American clients and help it catch up with industry leader Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co.
The world’s largest memory chip and smartphone maker is in discussions to locate a facility in Austin, Texas, capable of fabricating chips as advanced as 3 nanometers in the future, people familiar with the matter said. Plans are preliminary and subject to change but for now the aim is to kick off construction this year, install major equipment from 2022, then begin operations as early as 2023, they said. While the investment amount could fluctuate, Samsung’s plans would mean upwards of $10 billion to bankroll the project, one of the people said.
Samsung is taking advantage of a concerted U.S. government effort to counter China’s rising economic prowess and lure back home some of the advanced manufacturing that over the past decades has gravitated toward Asia. The hope is that such production bases in the U.S. will galvanize local businesses and support American industry and chip design. Intel Corp.’s troubles ramping up on technology and its potential reliance in the future on TSMC and Samsung for at least some of its chipmaking only underscored the extent to which Asian giants have forged ahead in recent years.
The envisioned plant will be its first in the U.S. to use extreme ultraviolet lithography, the standard for next-generation silicon, the people said, asking not to be identified talking about internal deliberations. Asked about plans for a U.S. facility, Samsung said in an email no decision has yet been made.
“If Samsung really wants to realize its goal to become the top chipmaker by 2030, it needs massive investment in the U.S. to catch up with TSMC,” said Greg Roh, senior vice president at HMC Securities. “TSMC is likely to keep making progress in process nodes to 3nm at its Arizona plant and Samsung may do the same. One challenging task is to secure EUV equipment now, when Hynix and Micron are also seeking to purchase the machines.”
If Samsung goes ahead, it would effectively go head-to-head on American soil with TSMC, which is on track to build its own $12 billion chip plant in Arizona by 2024. Samsung is trying to catch TSMC in the so-called foundry business of making chips for the world’s corporations -- a particularly pivotal capability given a deepening shortage of semiconductors in recent weeks.
Under Samsung family scion Jay Y. Lee, the company has said it wants to be the biggest player in the $400 billion chip industry. It plans to invest $116 billion into its foundry and chip design businesses over the next decade, aiming to catch TSMC by offering chips made using 3-nanometer technology in 2022.
It already dominates the market for memory chips and is trying to increase its presence in the more profitable market for logic devices, such as the processors that run smartphones and computers. It already counts Qualcomm Inc. and Nvidia Corp. as customers, companies that historically relied on TSMC exclusively. It has two EUV plants, one near its main chip site in Hwaseong, south of Seoul, and another coming online nearby at Pyeongtaek.
To close a deal, Samsung may need time to negotiate potential incentives with U.S. President Joe Biden’s administration. The company has hired people in Washington D.C. to lobby on behalf of the deal and is ready to go ahead with the new administration in place, the people said. Tax benefits and subsidies will ease Samsung’s financial burden, but the company may go ahead even without major incentives, one of the people said.
Samsung has been looking into overseas chipmaking for years. Intensifying trade tensions between the U.S. and China and now Covid-19 are stoking uncertainty over the reliability and economics of the global supply chain. Plants in the U.S. could help the Korean chipmaker strike better deals with key clients in the U.S., particularly in competition with TSMC.
From Microsoft Corp. to Amazon.com Inc. and Google, the world’s largest cloud computing firms are increasingly designing their own silicon to power their vast data centers more efficiently. All need manufacturers like TSMC or Samsung to turn their blueprints into reality.
Samsung’s U.S. branch purchased land in October next to its existing Austin fab, which is capable of running older processes. The Austin City Council held a meeting in December to discuss Samsung’s request to rezone that parcel of land for industrial development, according to meeting minutes.
The Korean company’s existing Texas facility is too small to to meet increasing orders for outsourced chips coming from Qualcomm, Intel and Tesla, according to research by Citibank. Intel in particular is likely to funnel more orders toward Samsung to offset any reliance on TSMC for its foundry needs, the brokerage said in a report.